How will public opinion on human-robot interactions change in the future?
19/01/2025 - 1:05
991 Words
Reading Time : 4min
Introduction
While AGI often dominates headlines, the concurrent rise of sophisticated robotics is equally transformative. These intertwined fields are rapidly reshaping society, from industry to personal assistance. This literature review explores how public opinion on human-robot interactions will likely evolve, considering factors such as safety, ethics, technological advancements, and media portrayals.
Abstract
This paper investigates human-robot interaction, analyzing current public perceptions (a mix of excitement and apprehension), technological advancements, and ethical and legal frameworks. It examines the impact of AI and robotics on sectors like healthcare and manufacturing, emphasizing the need for robust ethical guidelines and legal frameworks to ensure responsible and equitable integration of robots into society.
Discussion
Current Public Perception
Technological Advancements in Robotics and AGI
Public Opinion on Specific Applications
Legal and Ethical Frameworks for Robotics
Future Trends and Predictions
Studies indicate a generally positive public perception of robots, acknowledging their potential benefits across sectors. However, anxieties persist,
particularly regarding job displacement and the erosion of human control, especially in sectors like healthcare and childcare.1
While support for robot militarization exists, believing it enhances national security, this varies significantly across cultures.
For instance, Western concerns about robots challenging human specificity may be less prominent in Asian cultures, such as Japan.
Additionally, European citizens tend to hold more favorable views towards robots in manufacturing and security compared to healthcare and childcare.2 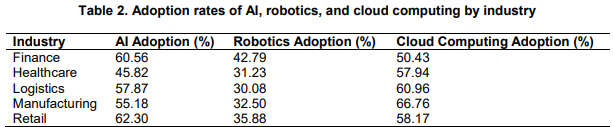
The evolution of robotics has been a remarkable journey, spanning centuries. From early conceptualizations like the mechanical birds of ancient Greece to the sophisticated robots of today, advancements have been driven by a combination of theoretical breakthroughs and technological innovation. 3
Foundational works like Karel Čapek's play R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots), which introduced the term 'robot' and explored the ethical implications of artificial beings, continue to influence our understanding of human-robot interaction. Asimov's Three Laws of Robotics, while often debated and challenged, provides a framework for considering the ethical guidelines that should govern the development and deployment of intelligent machines.4
Today, the field of robotics is experiencing unprecedented growth. We are witnessing the rise of sophisticated robots capable of performing complex tasks, from navigating challenging terrains (e.g., Boston Dynamics' Spot) to performing intricate surgeries (e.g., Intuitive Surgical's da Vinci system). Humanoid robots like Atlas are pushing the boundaries of human-like movement and dexterity, while companies like Tesla are exploring the integration of robotics with autonomous vehicles and Optimus.5 6
The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence, particularly in areas like machine learning and deep learning, are fueling this robotic revolution. From AGI-powered vision systems to advanced control algorithms, AGI is enabling robots to perceive their environment, make intelligent decisions, and interact with the world in increasingly sophisticated ways. This convergence of AGI and robotics is driving innovation across various sectors, from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and exploration.7
The development of brain-computer interfaces, exemplified by companies like Neuralink, further underscores the rapidly evolving landscape of human-robot interaction. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize how humans interact with machines and could lead to unprecedented levels of the concept explored by Lefebvre: Cybernanthope8 (human-machine symbiosis)
Research indicates that public opinion on specific robot applications varies significantly. While sectors such as security,
space exploration, and manufacturing are generally perceived as suitable domains for robotic deployment,
public acceptance in sectors like healthcare and childcare remains more nuanced. 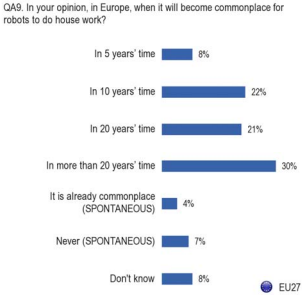 9
Studies have shown that direct experience with robots can positively influence public perception,
with individuals who initially expressed concerns demonstrating increased acceptance after interacting with robots in real-world settings
10. However, concerns about job displacement and the potential economic and social impacts of widespread automation remain significant.11
9
Studies have shown that direct experience with robots can positively influence public perception,
with individuals who initially expressed concerns demonstrating increased acceptance after interacting with robots in real-world settings
10. However, concerns about job displacement and the potential economic and social impacts of widespread automation remain significant.11
Recent studies suggest that the impact of automation may be more profound than previously anticipated, with some research pointing to the potential for increased inequality and the exacerbation of existing social and economic divides. While some argue that automation will primarily benefit high-skilled workers, concerns have been raised about the potential for job losses and declining wages for low-skilled workers.12 These concerns, often referred to as 'job displacement anxiety' or 'robot-phobia13,' highlight the need for proactive policies to mitigate the potential negative impacts of automation on the workforce keeping the future from becoming a "hyper-capitalist dystopia" or "socialist paradise".14 15
The rapid rate of technological advancement has raised concerns about a potential ethical and legal vacuum.16 This unprecedented success in the AGI and Robotics field risks outpacing the development of necessary ethical guidelines and legal frameworks. Without a proper foundation for the implementation of robotics across various sectors, the ethical and legal implications of these advancements could hinder their progress. Ensuring ethical and legal compliance is crucial for the safe and responsible integration of robotics into society.17
This concern is particularly acute in healthcare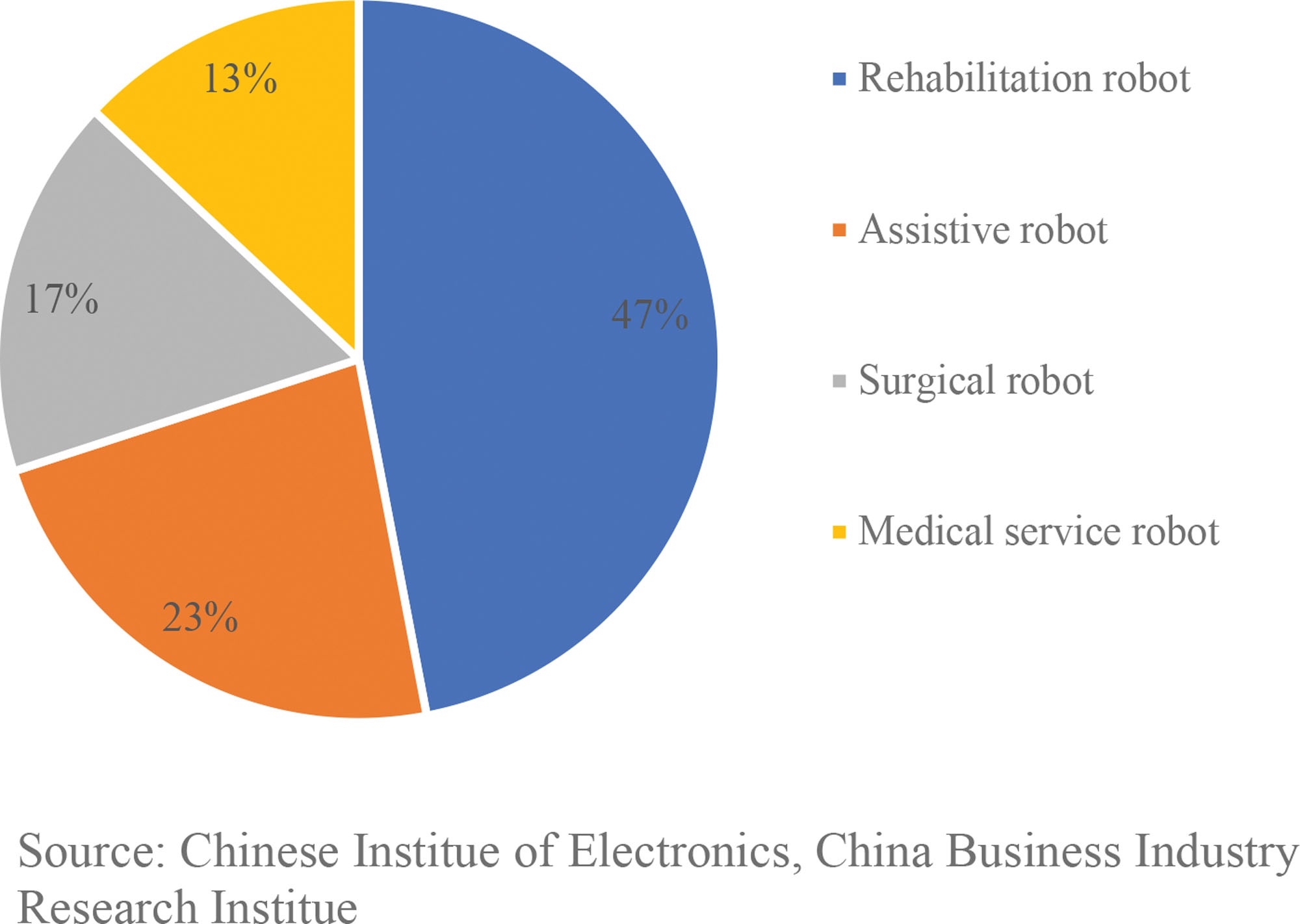 , where ethical and legal considerations are paramount.
The absence of robust legal frameworks and ethical guidelines poses a significant barrier to the safe and
responsible integration of robotics within this sector. This not only hinders technological advancement in
healthcare but also has broader implications for the entire robotics industry,
potentially impacting innovation and public trust across all sectors.18
, where ethical and legal considerations are paramount.
The absence of robust legal frameworks and ethical guidelines poses a significant barrier to the safe and
responsible integration of robotics within this sector. This not only hinders technological advancement in
healthcare but also has broader implications for the entire robotics industry,
potentially impacting innovation and public trust across all sectors.18
Failing to address these concerns can have serious consequences, such as jeopardized data privacy, algorithmic bias, and unclear legal and ethical protections for both users and developers. This can lead to situations where victims of robotic malfunctions are left without recourse, while the responsibility for harm remains unclear.19 20
The rapid advancement of robotics holds immense potential, but its success hinges on careful consideration of ethical, legal, and regulatory factors. Defining clear permissions and establishing ethical guidelines are crucial for widespread adoption. While job displacement is inevitable, those who embrace lifelong learning and adapt will thrive in this evolving landscape.
Conclusion
The future of human-robot interaction hinges on a balance between technological progress, public perception, and robust regulation. While concerns exist, the potential benefits are significant. Key actions include:
- Developing ethical guidelines and legal frameworks.
- Investing in workforce development.
- Fostering public dialogue. By proactively addressing these challenges, we can ensure a future where humans and robots coexist beneficially.
References
(x.) - Takes you back to the initial reference point in the literature review. (APA7 Citation) - Takes you to the source
Relevant imagery is referenced through use of matching colours
1. Javaheri, A., Moghadamnejad, N., Keshavarz, H., Javaheri, E., Dobbins, C., Momeni, E., & Rawassizadeh, R. (2019). Public vs media opinion on robots. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.01615.
2. Selesi-Aina, O., Obot, N. E., Olisa, A. O., Gbadebo, M. O., Olateju, O., & Olaniyi, O. O. (2024). The future of work: A human-centric approach to AI, robotics, and cloud computing. Journal of Engineering Research and Reports, 26(11), 10-9734.
3. Ilias Patsiaouras. (2024, June 6). History of Robots: From Fiction to Reality. Bota Systems. https://www.botasys.com/post/history-of-robots
4. Stanford University. (2019). Robotics: A Brief History. Stanford. https://cs.stanford.edu/people/eroberts/courses/soco/projects/1998-99/robotics/history.html
5. TerkRecoms - Tech TV. (2020). 9 Most Advanced AI Robots - Humanoid & Industrial Robots [YouTube Video]. In YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jky9I1ihAkg
6. GuizzoUpdated, E. (2018, August 1). Types of Robots. ROBOTS: Your Guide to the World of Robotics. https://robotsguide.com/learn/types-of-robots
7. Kumar, S. (2022, October 21). The role of AI in Robotics. https://www.aitude.com/the-role-of-ai-in-robotics/
8. Lefebvre, H. (1971). Vers le cybernanthrope. Henri Lefebvre.
9. Eurobarometer, S. (2012). Public attitudes towards robots. European Commission.
10. Shiomi, M., & Hagita, N. (2015, August). Social acceptance of a childcare support robot system. In 2015 24th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN) (pp. 13-18). IEEE.
11. Rotman, D. (2013). How technology is destroying jobs. Technology Review, 16(4), 28-35.
12. Cuccu, L., & Royuela, V. (2024). Just reallocated? Robots displacement, and job quality. British Journal of Industrial Relations, 62(4), 705-731. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjir.12805
13. Cai, R. (2024). Are robots stealing our jobs? Examining robot-phobia as a job stressor in the hospitality workplace. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, (ahead-of-print).
14. Lanchester, J. (2015). The robots are coming. London Review of Books, 37(5), 3-8.
15. Operto, S. (2019). Evaluating public opinion towards robots: a mixed-method approach. Paladyn, Journal of Behavioral Robotics, 10(1), 286-297. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjbr-2019-0023
16. Obaigbena, A., Lottu, O. A., Ugwuanyi, E. D., Jacks, B. S., Sodiya, E. O., & Daraojimba, O. D. (2024). AI and human-robot interaction: A review of recent advances and challenges. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews, 18(2), 321-330.
17. Akpuokwe, C. U., Adeniyi, A. O., & Bakare, S. S. (2024). Legal challenges of artificial intelligence and robotics: a comprehensive review. Computer Science & IT Research Journal, 5(3), 544-561.
18. Shentu, X. (2024). A review on legal issues of medical robots. Medicine, 103(21), e38330.
19. Mamak, K. (2024). Should criminal law protect love relation with robots?. AI & SOCIETY, 39(2), 573-582.
20. Razek, R. M. A. M. A. (2024). Criminal Responsibility for Errors Committed by Medical Robots: Legal and Ethical Challenges. Journal of Law and Sustainable Development, 12(1), e2443. https://doi.org/10.55908/sdgs.v12i1.2443